Starting a software company is no small feat. Not only do you need to come up with a great idea, but you also need to find the right team to help you bring it to life, create a business plan, and most importantly, raise capital.
For most software startups, raising capital is one of the biggest challenges. If you want to learn how to convince investors to fund your business, read on!
Why should startups raise capital?
Here are five reasons to get into the race for funding:
1. A software startup can greatly benefit from raising capital, as it can provide the resources needed to fuel growth and scale the business.
2. Capital can help a software startup hire the best talent, develop new products or features, and market itself effectively.
3. Raising capital can be essential for a software startup to succeed in today’s competitive landscape.
4. While there are risks associated with any form of fundraising, the potential rewards of raising capital make it a worthwhile endeavor for many software startups.
5. By carefully considering their options and planning for growth, software startups can increase their chances of success by tapping into new funding sources.
Why a financial model?
A financial model is a tool that can be used to predict the future financial performance of a company. But more importantly, numbers are the language of investors and financiers. If you want to convince them, you need to speak their language.
Financial models are generally created by investment banks and consulting firms for their clients. However, more and more companies are creating their in-house financial models to help make better business decisions.
There are many benefits of having a financial model. First, it can help a company make better decisions about where to invest its money. Second, a financial model can help a company track its progress over time and see how it performs relative to its peers. Finally, a financial model can help a company communicate its financial story to investors, analysts, and other stakeholders.
Step 1: understand your key assumptions
Before you can build a financial model, you need to understand your key assumptions. This includes understanding your marketing, revenue, expenses, and financing.
Your marketing defines how you get customers; i.e. this can happen through your website, email, ads, or sales reps. Your revenue is what will come in from selling your product or service. You need to know how much you will sell and at what price. Expenses are the costs of running your business. This includes things like CAPEX, labor, and overhead. Financing is how you’re going to pay for all of this. You need to know how much money you’re going to need to get started and where it’s going to come from.
Once you have a good understanding of your key assumptions, you can start building your financial model. This will help you figure out if your business is viable and make better decisions about how to run it.
Example from SaaS GIGA – Assumptions
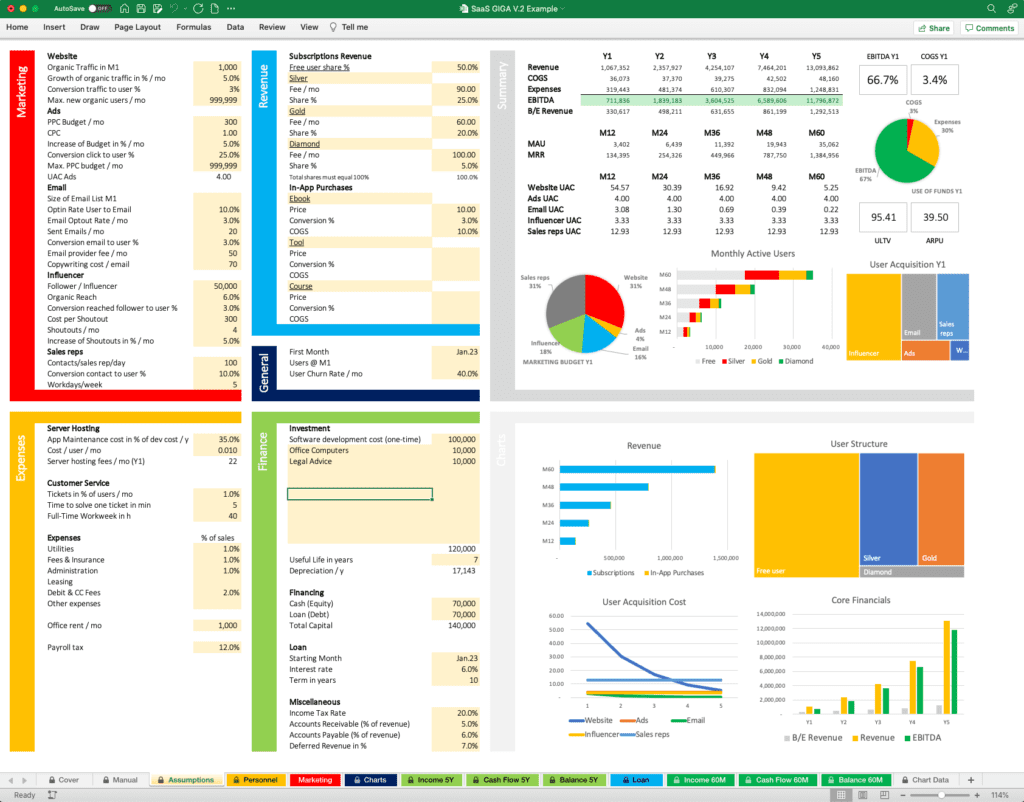
To make this topic more tangible, I will make an example with my financial model SaaS GIGA. The picture above shows the Assumptions page. The yellow cells are input cells where you can enter your assumptions. On the left, you find marketing, revenue, expenses, and finance. On the right, you get a summary of the most important results. Having assumptions and results on one page makes financial modeling much easier. When you enter a new assumption, i.e. a higher price for a subscription, you immediately see the impact on revenue and profit.
Step 2: build a sales forecast
As a software startup, one of the most important things you can do is build a sales forecast. This will help you determine how much revenue your business will generate and how quickly it will grow. Here are some tips on how to build a sales forecast for your software startup:
1. Know your subscription fees. This is one of the most important numbers in your forecast, as it will determine how much revenue you generate from each customer.
2. Estimate the number of customers you’ll have. This can be tricky but start by looking at your target market and estimating how many people would be interested in using your software.
3. Growth rates matter. Be realistic about the growth rate of your business. If you’re expecting too much too soon, you may be disappointed (and run out of cash).
Example from SaaS GIGA – Marketing and Revenue
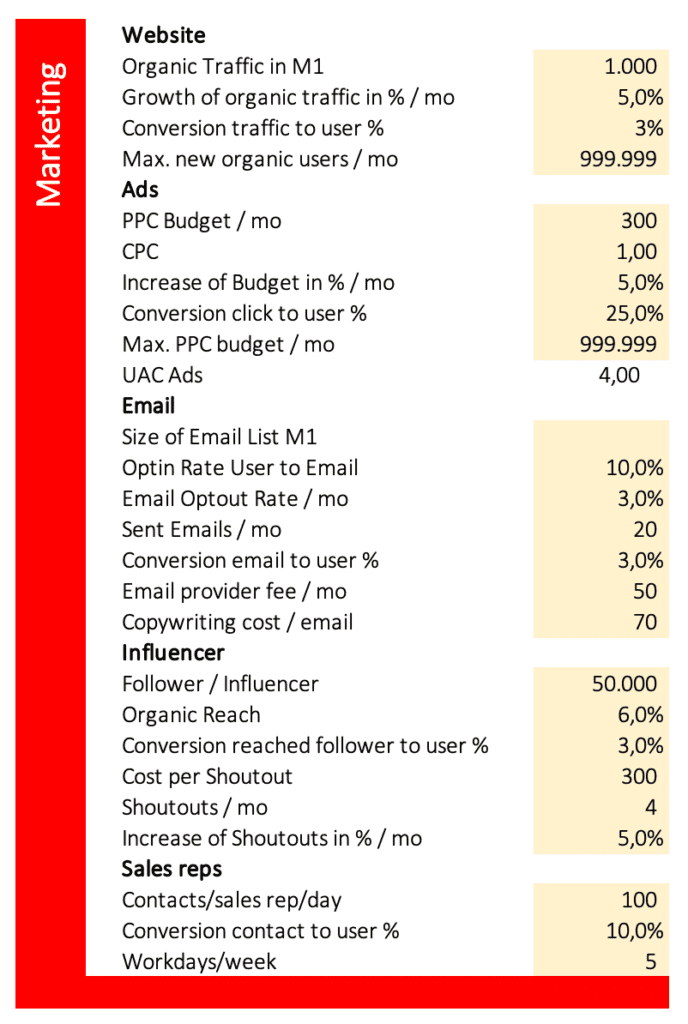
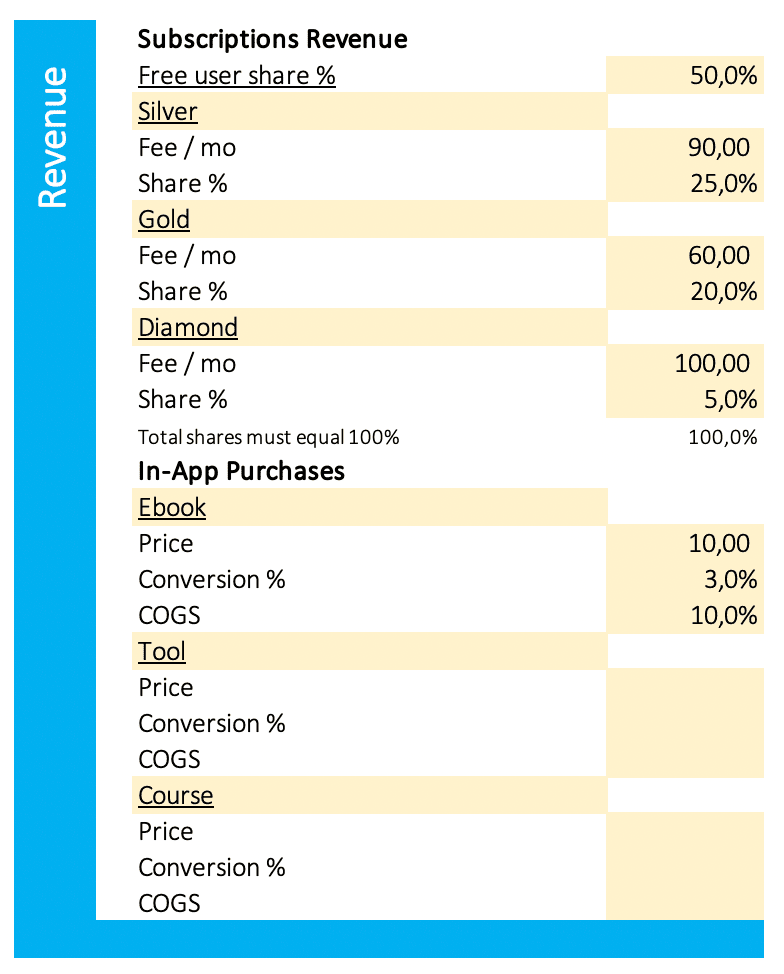
My SaaS financial model goes one step further, as you can build up your customer base by determining your marketing strategies. The idea is that your marketing activities will create users.
You can define traffic and conversion of your website, which will result in users. In this example, organic traffic from search engines is 1000 visitors in month one, and the conversion rate of traffic to users is 3%. So in month one, the business gains 30 users from 1000 visitors (1000 * 3% = 30). You can further assume the growth of organic traffic with i.e. 5% per month.
In SaaS GIGA, you can further plan marketing by ads, email, influencers, and sales reps. Within the revenue section, you can define the share of free users, three different subscription plans, and one-time in-app purchases like ebooks, tools, and courses. Enter a monthly fee for each subscription and a share in percent of all users. In the example, 25% of all users buy the “Silver” subscription, which equals a share of 25%. As the sum of all users has to be 100%, the sum of free users and all three subs must also be 100%.
In the example, 3% of all users buy the ebook for $10.
The churn rate in the “General” section is a major revenue driver. The longer your customers stay loyal, the lower your churn rate. To calculate churn, divide 100% by the number of months the average subscriber uses your software. I.e. average duration of using your software is 2.5 months; 100% / 2.5 months = 40% churn rate.
Step 3: calculate your costs
As a software startup, one of your primary concerns is going to be costs. Specifically, you need to calculate the costs of server hosting, customer service, expenses, office rent, and payroll tax. Here’s how to do it:
1. Server hosting: You’ll need to factor in the cost of renting or owning servers, as well as the cost of bandwidth and data storage. Make sure to include both fixed and variable costs in your calculations.
2. Customer service: The cost of customer service will include things like call center staffing, support staff salaries, and any other associated expenses.
3. Expenses: This category includes all the miscellaneous expenses that come with running a business, from office supplies to legal fees.
Example from SaaS GIGA – Expenses

In SaaS GIGA, you can plan all typical expenses. To calculate the costs for server hosting, determine the cost per user per month, i.e. $0.01. This cost can vary wildly and depends very much on the used bandwidth. Further, you can consider app maintenance cost in percent of development cost per year. The reference value is about 20 to 50% per year.
Customer service depends on the needed amount of tickets in percent of users and the time to solve one ticket in minutes. In the example, 1% of users need customer service per month, and the average time to solve is 5 minutes.
Expenses like utilities, fees, insurance, administration, leasing, debit and credit card fees, and other expenses can be defined by a percentage of sales.
For office rent, you can enter a certain amount per month.
A percentage of salaries can calculate payroll tax.
For staffing, SaaS GIGA provides the assumptions tab “Personnel”, where you can define all employee positions and the number of employees for each position and month. The number of sales reps will impact the revenue generated by sales reps.
Step 4: calculate your profits
If you want to calculate the profits for a software startup, there are a few key things that you will need to take into account. The first is revenue. This is the total amount of money the company has brought in through sales of its products or services. The second is COGS or cost of goods sold. This includes the costs associated with producing and selling the software. The third is expenses, which are all the other costs that the company incurs in its day-to-day operations. Finally, you will need to calculate EBITDA, or earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. This number represents the company’s profitability before taking into account any of these other factors. To calculate profits, simply take revenue and subtract COGS and expenses. This will give you your operating profit or loss.
Example from SaaS GIGA – Summary of core financials
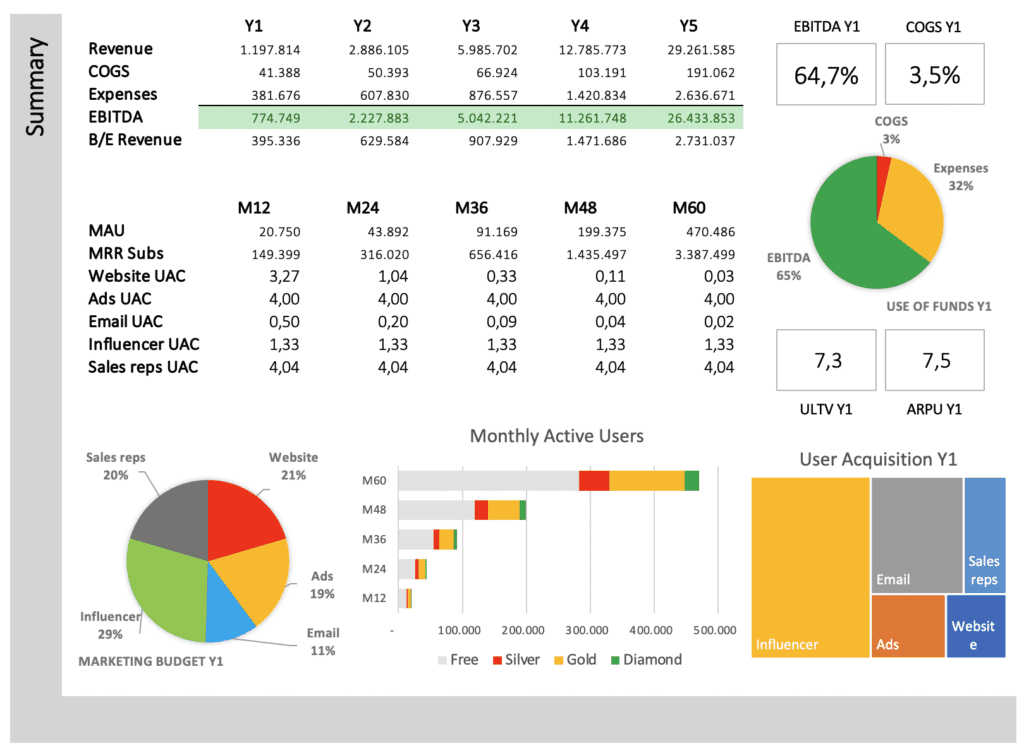
SaaS GIGA provides a summary of all core financial results on the assumptions page and detailed data for five years, yearly and monthly, in separate tabs.
MAU is monthly active users. MRR represents monthly recurring revenue. UAC is user acquisition cost for each marketing campaign. ULTV is user lifetime value. ARPU is the average revenue per user. If UAC is lower than ULTV, a certain marketing campaign is profitable. Several charts give deeper insights into your business model.

Step 5: raise money from investors
No one will invest in your company unless you can present a convincing case for why your business will be successful. Here are some tips on how to raise money for your startup by creating a presentation that will impress potential investors. Before you start pitching to investors, you need to have a solid financial model that shows how your business will make money. This model should include projections for revenue, expenses, and profitability. Once you have this information, you can start creating your presentation. When making your presentation, remember to keep it simple and focus on the key points that will convince investors to give you funding. Make sure to highlight the potential return on investment and stress how your software startup will solve a problem or meet a need in the marketplace.
SaaS GIGA can help you with this task. After entering your assumptions and creating your business case, you can make screenshots from the financial model and insert them into your pitch deck. This will provide not only convincing data but also a professional look and feel.
Conclusion
A financial model can be a powerful tool for raising capital. By clearly articulating your company’s financial story, you can give investors the confidence they need to invest in your business. With a well-crafted financial model, you can make the case for why your company is a good investment and attract the capital you need to grow your business.
Not sure which template is the right one for your business? No problem! Join me in a free Zoom call, and let´s find out which solution is perfect for you. You can choose from various templates, and I also offer services for customization and onboarding.
Content that you may also like:
Tips for a convincing pitch deck
- Start with a strong title slide
- Make sure your slides are visually appealing
- Keep your pitch deck concise
- Highlight your key points
- Tell a story
- Practice, practice, practice
Peter is a solopreneur in Salzburg, Austria, a husband, and a family father. He runs a little publishing company, and blogs about starting and running online businesses. In his spare time, he enjoys hiking with friends and reading the Bible, and sometimes he takes a trip in his roaring old black 2001 Jaguar XJ8.